The Machinery Regulation will be mandatory in less than a year — are you ready?

The countdown is on! The EU Machinery Regulation (EU 2023/1230) becomes mandatory in less than a year, on 20 January 2027, and the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) follows closely behind with full compliance required by 11 December 2027. CRA reporting obligations for vulnerabilities and severe incidents start even earlier — on 11 September 2026.
These two regulations will reshape how manufacturers and operators approach safety and cybersecurity. The question is: are you ready?
Why these regulations matter and how to prepare
The Machinery Regulation introduces a groundbreaking principle: No safety without security. Machines are no longer isolated; they are connected to networks, making them vulnerable to cyber threats.
A safety function is only valid if it cannot be compromised. Similarly, CRA ensures that connected products meet strict cybersecurity requirements, reinforcing resilience across the entire industrial ecosystem.
Six steps to industrial security: What companies should do now
- Carry out a risk analysis: Begin by identifying all critical assets in your machinery and control systems. Ask which assets are worth protecting and what is the worst-case scenario if they are compromised, and document potential attack paths then prioritise based on impact.
- Integrate security into the safety strategy: Safety functions must not only work under normal conditions but also remain secure against manipulation. Review your safety architecture and embed security measures such as identity and access authentication and integrity checks.
- Increase communication with operators: Operators know the real-world application scenarios and risks better than anyone. Establish regular communication channels to share insights on vulnerabilities, misuse risks, and operational challenges.
- Set up a firewall and access protection: Implement network segmentation to separate critical control systems from external networks. Use firewalls, VPNs, and strict access control policies to prevent unauthorised entry. Ensure remote access is secure and monitored.
- Comply with standards and laws: Familiarise yourself with CRA, NIS 2, and the Machinery Regulation requirements. These define clear obligations for cybersecurity, vulnerability management and secure-by-design principles. Align your processes now to avoid last-minute compliance issues.
- Evaluate security cyclically: Security is not a one-time task. Threats evolve, so schedule regular reviews and updates to your risk assessments, patch management, and security controls. Adopt a continuous improvement mindset.
Implementing these steps now will help you prepare for the future — avoiding downtime, preventing cyberattacks, and ensuring a smooth compliance process before deadlines.
How Pilz supports industrial security compliance
Pilz is helping businesses take the complexity out of industrial security compliance. With regulations tightening and cyber threats on the rise, manufacturers and operators need more than just basic safeguards — they need a complete strategy that blends safety and security seamlessly.
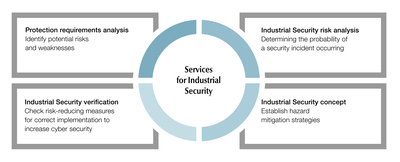
That’s where Pilz comes in. Through its Industrial Security Consulting Service, Pilz guides companies step by step: from analysing protection requirements and assessing risks to developing tailored security concepts and verifying their effectiveness. This structured approach ensures that security isn’t an afterthought but an integral part of the machine lifecycle.
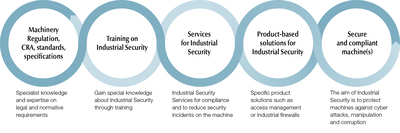
Pilz’s strength lies in its deep knowledge of international standards such as IEC 62443 and the forthcoming EN 50742, giving businesses confidence that they’re meeting the latest compliance requirements.
Beyond consulting, Pilz invests in building customer competence through dedicated training programmes. Courses such as Fundamentals of Industrial Security and CESA – Certified Expert for Security in Automation are designed to combine theoretical knowledge with practical examples, while deepening understanding of relevant regulations like IEC 62443. Successful CESA candidates qualify as recognised security experts for industrial automation systems, equipping them to implement robust security concepts in practice.
Pilz also provides product-based security solutions that integrate seamlessly with safety systems. This combination of consulting, training, and technology creates a comprehensive, future-proof security framework that helps businesses stay compliant and resilient in an increasingly connected industrial world.
With deadlines like January and December 2027 fast approaching, Pilz is encouraging businesses to act now.
The missing middle: Solving the logic solver gap in SIS design
Why safety professionals need a new class of logic solver; one that bridges the enormous gap...
Pilz delivers compliant access management system at Schüco's testing facility
Schüco envisioned a centralised permissions management system that would streamline access...
High Integrity Pressure Protection System (HIPPS) 2oo3 voting shutdown system
The Moore Industries SLA Multiloop and Multifunctional Logic Solver plays a pivotal role in...











